Date:16/10/18
 Virtual reality motion controllers work pretty well at syncing up the movements of digital digits with your real ones, but they aren't all that good at recreating the sense of touch. Scientists from EPFL and ETH Zurich have developed new haptic gloves that could help users get in touch with virtual objects.
Virtual reality motion controllers work pretty well at syncing up the movements of digital digits with your real ones, but they aren't all that good at recreating the sense of touch. Scientists from EPFL and ETH Zurich have developed new haptic gloves that could help users get in touch with virtual objects.
Haptic feedback systems aren't particularly new. We've seen them crammed into gloves, boots, jackets, and even full-body suits, and made real through vibrating motors, inflatable bladders, electrical fields or just mechanical components that push back.
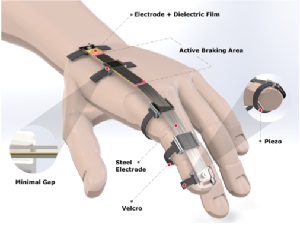
The new gloves, dubbed DextrES, work using a pretty novel technique. Embedded into the fingers of nylon gloves are strips of an elastic metal with a thin insulator between them. When a virtual object needs to be simulated, a voltage difference is applied to the metal strips, which causes them to stick together. That in turn creates a braking force – the wearer physically can't close their fingers past a certain point, giving them the firm impression that there's something in their hand. When the object is dropped, the voltage is lifted and they can move their fingers freely again.
The DextrES haptic gloves work thanks to metal strips in the fingers, which can block movements...
"The human sensory system is highly developed and highly complex," says Otmar Hilliges, head of the Advanced Interactive Technologies Lab at ETH Zurich. "We have many different kinds of receptors at a very high density in the joints of our fingers and embedded in the skin. As a result, rendering realistic feedback when interacting with virtual objects is a very demanding problem and is currently unsolved. Our work goes one step in this direction, focusing particularly on kinesthetic feedback."
To test DextrES, the team had participants perform virtual reality tasks that required fine motor skills, and the feedback was apparently positive. Along with the realistic recreations, the gloves are far less bulky than other systems, being only 2 mm (0.08 in) thick and with the equipment weighing just 8 g (0.3 oz) per finger.
The system can apply up to 40 Newtons of force on each finger using just 200 volts and a few milliwatts of power. In its current form it's powered through external cables, but given that low power requirement the team says it could fairly easily be adapted to run off a small battery.
"We wanted to develop a lightweight device that – unlike existing virtual-reality gloves – doesn't require a bulky exoskeleton, pumps or very thick cables," says Herbert Shea, head of the Soft Transducers Laboratory at EPFL.
Light, thin VR gloves put wearers in touch with virtual objects
 Virtual reality motion controllers work pretty well at syncing up the movements of digital digits with your real ones, but they aren't all that good at recreating the sense of touch. Scientists from EPFL and ETH Zurich have developed new haptic gloves that could help users get in touch with virtual objects.
Virtual reality motion controllers work pretty well at syncing up the movements of digital digits with your real ones, but they aren't all that good at recreating the sense of touch. Scientists from EPFL and ETH Zurich have developed new haptic gloves that could help users get in touch with virtual objects.Haptic feedback systems aren't particularly new. We've seen them crammed into gloves, boots, jackets, and even full-body suits, and made real through vibrating motors, inflatable bladders, electrical fields or just mechanical components that push back.
The new gloves, dubbed DextrES, work using a pretty novel technique. Embedded into the fingers of nylon gloves are strips of an elastic metal with a thin insulator between them. When a virtual object needs to be simulated, a voltage difference is applied to the metal strips, which causes them to stick together. That in turn creates a braking force – the wearer physically can't close their fingers past a certain point, giving them the firm impression that there's something in their hand. When the object is dropped, the voltage is lifted and they can move their fingers freely again.
The DextrES haptic gloves work thanks to metal strips in the fingers, which can block movements...
"The human sensory system is highly developed and highly complex," says Otmar Hilliges, head of the Advanced Interactive Technologies Lab at ETH Zurich. "We have many different kinds of receptors at a very high density in the joints of our fingers and embedded in the skin. As a result, rendering realistic feedback when interacting with virtual objects is a very demanding problem and is currently unsolved. Our work goes one step in this direction, focusing particularly on kinesthetic feedback."
To test DextrES, the team had participants perform virtual reality tasks that required fine motor skills, and the feedback was apparently positive. Along with the realistic recreations, the gloves are far less bulky than other systems, being only 2 mm (0.08 in) thick and with the equipment weighing just 8 g (0.3 oz) per finger.
The system can apply up to 40 Newtons of force on each finger using just 200 volts and a few milliwatts of power. In its current form it's powered through external cables, but given that low power requirement the team says it could fairly easily be adapted to run off a small battery.
"We wanted to develop a lightweight device that – unlike existing virtual-reality gloves – doesn't require a bulky exoskeleton, pumps or very thick cables," says Herbert Shea, head of the Soft Transducers Laboratory at EPFL.
Views: 690
©ictnews.az. All rights reserved.Similar news
- The mobile sector continues its lead
- Facebook counted 600 million active users
- Cell phone testing laboratory is planned to be built in Azerbaijan
- Tablets and riders outfitted quickly with 3G/4G modems
- The number of digital TV channels will double to 24 units
- Tax proposal in China gets massive online feedback
- Malaysia to implement biometric system at all entry points
- Korea to build Green Technology Centre
- Cisco Poised to Help China Keep an Eye on Its Citizens
- 3G speed in Azerbaijan is higher than in UK
- Government of Canada Announces Investment in Green Innovation for Canada
- Electric cars in Azerbaijan
- Dominican Republic Govt Issues Cashless Benefits
- Spain raises €1.65bn from spectrum auction
- Camden Council boosts mobile security