Date:30/09/16
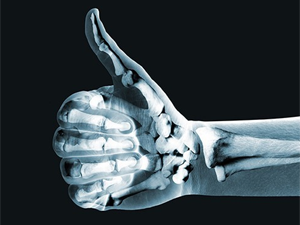 A team of researchers from Northwestern University have developed a 3D-printable ink that produces synthetic bone material, which they hope will ease the lives of children needing implantation surgery in the future.
A team of researchers from Northwestern University have developed a 3D-printable ink that produces synthetic bone material, which they hope will ease the lives of children needing implantation surgery in the future.
The study, published in Science Translational Medicine, produced a hyperelastic bone-like material that can be easily customized to fit the needs of its host. Currently, bone implantation surgery typically involves harvesting needed bone from elsewhere in the body, which can cause additional complications and pain. Lead researcher Ramille Shah says this places a particular strain on growing children who need repeated surgeries as they age.
"Adults have more options when it comes to implants," Shah said in a press release. "Pediatric patients do not. If you give them a permanent implant, you have to do more surgeries in the future as they grow. They might face years of difficulty."
The 3D-printed synthetic bone material used in the study was made using a mix of hydroxyapatite, a calcium mineral found in natural human bone, with a biodegradable polymer. Researchers evaluated the material with stem cells and within animal models.
"Cells can sense the hydroxyapatite and respond to its bioactivity," Shah added. "When you put stem cells on our scaffolds, they turn into bone cells and start to up-regulate their expression of bone specific genes. This is in the absence of any other osteo-inducing substances. It's just the interaction between the cells and the material itself."
Northwestern's research team also experimented by combining other materials into the ink, including antibiotics. Shah says the biggest advantage of their new product is its ability to be customized for patients.
"The turnaround time for an implant that's specialized for a customer could be within 24 hours. That could change the world of craniofacial and orthopaedic surgery, and, I hope, will improve patient outcomes," she said.
Researchers develop material for 3D-printing bone
 A team of researchers from Northwestern University have developed a 3D-printable ink that produces synthetic bone material, which they hope will ease the lives of children needing implantation surgery in the future.
A team of researchers from Northwestern University have developed a 3D-printable ink that produces synthetic bone material, which they hope will ease the lives of children needing implantation surgery in the future.The study, published in Science Translational Medicine, produced a hyperelastic bone-like material that can be easily customized to fit the needs of its host. Currently, bone implantation surgery typically involves harvesting needed bone from elsewhere in the body, which can cause additional complications and pain. Lead researcher Ramille Shah says this places a particular strain on growing children who need repeated surgeries as they age.
"Adults have more options when it comes to implants," Shah said in a press release. "Pediatric patients do not. If you give them a permanent implant, you have to do more surgeries in the future as they grow. They might face years of difficulty."
The 3D-printed synthetic bone material used in the study was made using a mix of hydroxyapatite, a calcium mineral found in natural human bone, with a biodegradable polymer. Researchers evaluated the material with stem cells and within animal models.
"Cells can sense the hydroxyapatite and respond to its bioactivity," Shah added. "When you put stem cells on our scaffolds, they turn into bone cells and start to up-regulate their expression of bone specific genes. This is in the absence of any other osteo-inducing substances. It's just the interaction between the cells and the material itself."
Northwestern's research team also experimented by combining other materials into the ink, including antibiotics. Shah says the biggest advantage of their new product is its ability to be customized for patients.
"The turnaround time for an implant that's specialized for a customer could be within 24 hours. That could change the world of craniofacial and orthopaedic surgery, and, I hope, will improve patient outcomes," she said.
Views: 552
©ictnews.az. All rights reserved.Similar news
- Azerbaijani project to monitor disease via mobile phones
- Innovative educational system to be improved under presidential decree
- NTRC prolongs license of two TV and radio organizations for 6 years
- Azerbaijan establishes e-registry for medicines
- Azerbaijani museum introduces e-guide
- Nar Mobile opens “Nar Dunyasi” sales and service center in Siyazan city
- International conference on custom electronic services held in Baku
- OIC secretary general to attend COMSTECH meeting in Baku
- Azerbaijan develops earthquake warning system
- New law to regulate transition to digital broadcasting in Azerbaijan
- Azerbaijani State Social Protection Fund introduces electronic digital signature
- Intellectual traffic management system in Baku to be commissioned in December
- Tax Ministry of Azerbaijan started receiving video-addresses
- World Bank recommends Azerbaijan to speed up e-service introduction in real estate
- Azerbaijan to shift to electronic registration of real estate