Date:30/03/18
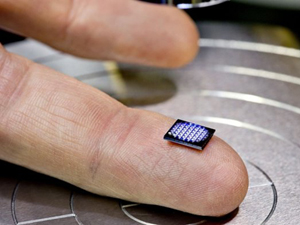 The miniaturization of electronics has been progressing steadily for decades, but IBM just took a major leap. The company has created what it’s calling the world’s smallest computer, and it’s the size of a grain of salt.
The miniaturization of electronics has been progressing steadily for decades, but IBM just took a major leap. The company has created what it’s calling the world’s smallest computer, and it’s the size of a grain of salt.
The 1 millimeter x 1 millimeter device was unveiled at the computing giant’s IBM Think 2018 conference. Despite its diminutive size, the company claims the computer has the same amount of power as an x86 chip from 1990, which The Verge points out means it’s probably just about powerful enough to play the computer game Doom.
Unsurprisingly, though, IBM has bigger plans for it than that. The company sees the tiny computer becoming a crucial element of attempts to apply blockchain to supply chain management by collecting, processing, and communicating data on goods being shipped around the country.
To enable this, the device features a processor with “several hundred thousand” transistors, SRAM memory, a communications unit that consists of an LED that can send messages by blinking, and a photodetector that can pick up optical signals. Plugging such a tiny device into the mains is clearly not feasible, so it comes with a photovoltaic cell to power it.
Costing less than 10 cents to manufacture, the company envisions the device being embedded into products as they move around the supply chain. The computer’s sensing, processing, and communicating capabilities mean it could effectively turn every item in the supply chain into an Internet of Things device, producing highly granular supply chain data that could streamline business operations.
But more importantly, the computer could be a critical element of IBM’s efforts to apply blockchain technology to the supply chain. The company is going all in on the technology and is working with a number of large companies to use the computer to tackle everything from food supply to insurance. This week they also launched a simpler and cheaper “blockchain starter plan” aimed at start-ups and those just beginning to experiment with the technology.
Supply chain management is one of the killer apps for the technology. Blockchain is essentially a distributed ledger that can be used to track everything from transactions to inventory. Identical copies of the ledger are kept on all computers participating in the network.
Every time a new record, or block, is added to the ledger, it includes a cryptographic hash that links it back to the previous block, creating an uninterrupted chain that can be followed all the way back to the first block. Once a new block has been added to the chain all of the participants get an updated copy of the ledger, so it’s nearly impossible to tamper with, as you’d have to edit all the copies simultaneously.
The benefits of this approach are enormous for supply chain management. Previously, you’d have multiple stakeholders from suppliers to couriers to clients all using different ways of tracking items, processes, and transactions. With the blockchain all of this can be recorded in a shared ledger that updates in real time, provides every participant with the same visibility, and is entirely traceable.
Unlike tracking banking transactions or contracts, though, for the approach to work for supply chain it needs to be able to interact with the physical goods themselves. That’s where IBM’s tiny computer comes in.
The company has been working on what it calls crypto-anchors, which it describes as “tamper-proof digital fingerprints, to be embedded into products, or parts of products, and linked to the blockchain.”
These anchors carry a cryptographic message linked back to the blockchain that can be used to identify and authenticate the product. This message can be encoded in various ways; another approach the company has investigated is using edible magnetic ink to create patterns of colored dots on medicines.
But the benefit of the mini computer is that it can also collect and analyze data as it passes through the supply chain. That means as well as helping verify the product’s provenance, it could potentially give stakeholders insight into how it’s been handled or whether there’s been any attempt to tamper with it.
The tiny computer is currently a prototype, and there’s still little detail on how exactly the computer will be linked to the blockchain. But the company says it plans to start rolling out its crypto-anchor solution in the next 18 months. So keep an eye out—it may not be long before the world’s smallest computer is delivered to your door.
IBM’s New Computer Is the Size of a Grain of Salt and Costs Less Than 10 Cents
 The miniaturization of electronics has been progressing steadily for decades, but IBM just took a major leap. The company has created what it’s calling the world’s smallest computer, and it’s the size of a grain of salt.
The miniaturization of electronics has been progressing steadily for decades, but IBM just took a major leap. The company has created what it’s calling the world’s smallest computer, and it’s the size of a grain of salt.The 1 millimeter x 1 millimeter device was unveiled at the computing giant’s IBM Think 2018 conference. Despite its diminutive size, the company claims the computer has the same amount of power as an x86 chip from 1990, which The Verge points out means it’s probably just about powerful enough to play the computer game Doom.
Unsurprisingly, though, IBM has bigger plans for it than that. The company sees the tiny computer becoming a crucial element of attempts to apply blockchain to supply chain management by collecting, processing, and communicating data on goods being shipped around the country.
To enable this, the device features a processor with “several hundred thousand” transistors, SRAM memory, a communications unit that consists of an LED that can send messages by blinking, and a photodetector that can pick up optical signals. Plugging such a tiny device into the mains is clearly not feasible, so it comes with a photovoltaic cell to power it.
Costing less than 10 cents to manufacture, the company envisions the device being embedded into products as they move around the supply chain. The computer’s sensing, processing, and communicating capabilities mean it could effectively turn every item in the supply chain into an Internet of Things device, producing highly granular supply chain data that could streamline business operations.
But more importantly, the computer could be a critical element of IBM’s efforts to apply blockchain technology to the supply chain. The company is going all in on the technology and is working with a number of large companies to use the computer to tackle everything from food supply to insurance. This week they also launched a simpler and cheaper “blockchain starter plan” aimed at start-ups and those just beginning to experiment with the technology.
Supply chain management is one of the killer apps for the technology. Blockchain is essentially a distributed ledger that can be used to track everything from transactions to inventory. Identical copies of the ledger are kept on all computers participating in the network.
Every time a new record, or block, is added to the ledger, it includes a cryptographic hash that links it back to the previous block, creating an uninterrupted chain that can be followed all the way back to the first block. Once a new block has been added to the chain all of the participants get an updated copy of the ledger, so it’s nearly impossible to tamper with, as you’d have to edit all the copies simultaneously.
The benefits of this approach are enormous for supply chain management. Previously, you’d have multiple stakeholders from suppliers to couriers to clients all using different ways of tracking items, processes, and transactions. With the blockchain all of this can be recorded in a shared ledger that updates in real time, provides every participant with the same visibility, and is entirely traceable.
Unlike tracking banking transactions or contracts, though, for the approach to work for supply chain it needs to be able to interact with the physical goods themselves. That’s where IBM’s tiny computer comes in.
The company has been working on what it calls crypto-anchors, which it describes as “tamper-proof digital fingerprints, to be embedded into products, or parts of products, and linked to the blockchain.”
These anchors carry a cryptographic message linked back to the blockchain that can be used to identify and authenticate the product. This message can be encoded in various ways; another approach the company has investigated is using edible magnetic ink to create patterns of colored dots on medicines.
But the benefit of the mini computer is that it can also collect and analyze data as it passes through the supply chain. That means as well as helping verify the product’s provenance, it could potentially give stakeholders insight into how it’s been handled or whether there’s been any attempt to tamper with it.
The tiny computer is currently a prototype, and there’s still little detail on how exactly the computer will be linked to the blockchain. But the company says it plans to start rolling out its crypto-anchor solution in the next 18 months. So keep an eye out—it may not be long before the world’s smallest computer is delivered to your door.
Views: 534
©ictnews.az. All rights reserved.Similar news
- The mobile sector continues its lead
- Facebook counted 600 million active users
- Cell phone testing laboratory is planned to be built in Azerbaijan
- Tablets and riders outfitted quickly with 3G/4G modems
- The number of digital TV channels will double to 24 units
- Tax proposal in China gets massive online feedback
- Malaysia to implement biometric system at all entry points
- Korea to build Green Technology Centre
- Cisco Poised to Help China Keep an Eye on Its Citizens
- 3G speed in Azerbaijan is higher than in UK
- Government of Canada Announces Investment in Green Innovation for Canada
- Electric cars in Azerbaijan
- Dominican Republic Govt Issues Cashless Benefits
- Spain raises €1.65bn from spectrum auction
- Camden Council boosts mobile security