Date:02/02/19
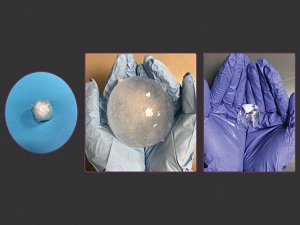 The soft, squishy device, which is made from hydrogel materials, is softer, longer lasting and more biocompatible than some of the current ingestible stomach sensors that can only stay in the stomach for a few days.
The soft, squishy device, which is made from hydrogel materials, is softer, longer lasting and more biocompatible than some of the current ingestible stomach sensors that can only stay in the stomach for a few days.
Lin and colleagues wanted to design a hydrogel-based pill that could be used to carry sensors into the stomach to monitor vital signs or disease states over an extended period.
However, they knew that a pill tiny enough to pass down the esophagus and into the stomach would also be small enough to pass through a structure called the pylorus and out of the stomach.
They therefore looked at ways of designing a pill that would quickly expand to the size of a ping-pong ball to prevent it from leaving the stomach.
The inflatable device is made up of one inner hydrogel layer containing superabsorbent particles that quickly soak up liquid and expand and a second outer layer that forms a protective layer that is impervious to churning stomach acids.
As reported in the journal Nature Communications, on immersing the pill in solutions that mimicked gastric juices, the pill expanded to 100 times its original size within about one-quarter of an hour, which is much faster than the rate seen with existing hydrogel-based devices. Senior author Xuanhe Zhao says that once inflated, the pill resembles the softness of Jell-O, but is surprisingly strong.
To test the strength of the pill, the team squeezed it thousands of times, applying forces even greater than those it would be subjected to as the stomach contracts.
“We found that even when we make a small cut in the membrane, and then stretch and squeeze it thousands of times, the cut does not grow larger. Our design is very robust,” says Lin.
Finally, small temperature sensors were embedded in the pill which was then fed to pigs. The sensors were later retrieved from the pigs’ stool and used to plot temperature measurements over time.
The team reports that the sensors were accurate at tracking the pigs’ daily activity over a period of 30 days.
Liu and colleagues hope the pill could one day be used to deliver sensors to the stomach that could measure pH levels and signs of bacterial or viral infection, for example, or cameras that could capture images of ulcers or tumors.
Expanding pill could be used to monitor stomach conditions for up to one month
 The soft, squishy device, which is made from hydrogel materials, is softer, longer lasting and more biocompatible than some of the current ingestible stomach sensors that can only stay in the stomach for a few days.
The soft, squishy device, which is made from hydrogel materials, is softer, longer lasting and more biocompatible than some of the current ingestible stomach sensors that can only stay in the stomach for a few days.Lin and colleagues wanted to design a hydrogel-based pill that could be used to carry sensors into the stomach to monitor vital signs or disease states over an extended period.
However, they knew that a pill tiny enough to pass down the esophagus and into the stomach would also be small enough to pass through a structure called the pylorus and out of the stomach.
They therefore looked at ways of designing a pill that would quickly expand to the size of a ping-pong ball to prevent it from leaving the stomach.
The inflatable device is made up of one inner hydrogel layer containing superabsorbent particles that quickly soak up liquid and expand and a second outer layer that forms a protective layer that is impervious to churning stomach acids.
As reported in the journal Nature Communications, on immersing the pill in solutions that mimicked gastric juices, the pill expanded to 100 times its original size within about one-quarter of an hour, which is much faster than the rate seen with existing hydrogel-based devices. Senior author Xuanhe Zhao says that once inflated, the pill resembles the softness of Jell-O, but is surprisingly strong.
To test the strength of the pill, the team squeezed it thousands of times, applying forces even greater than those it would be subjected to as the stomach contracts.
“We found that even when we make a small cut in the membrane, and then stretch and squeeze it thousands of times, the cut does not grow larger. Our design is very robust,” says Lin.
Finally, small temperature sensors were embedded in the pill which was then fed to pigs. The sensors were later retrieved from the pigs’ stool and used to plot temperature measurements over time.
The team reports that the sensors were accurate at tracking the pigs’ daily activity over a period of 30 days.
Liu and colleagues hope the pill could one day be used to deliver sensors to the stomach that could measure pH levels and signs of bacterial or viral infection, for example, or cameras that could capture images of ulcers or tumors.
Views: 660
©ictnews.az. All rights reserved.Similar news
- The mobile sector continues its lead
- Facebook counted 600 million active users
- Cell phone testing laboratory is planned to be built in Azerbaijan
- Tablets and riders outfitted quickly with 3G/4G modems
- The number of digital TV channels will double to 24 units
- Tax proposal in China gets massive online feedback
- Malaysia to implement biometric system at all entry points
- Korea to build Green Technology Centre
- Cisco Poised to Help China Keep an Eye on Its Citizens
- 3G speed in Azerbaijan is higher than in UK
- Government of Canada Announces Investment in Green Innovation for Canada
- Electric cars in Azerbaijan
- Dominican Republic Govt Issues Cashless Benefits
- Spain raises €1.65bn from spectrum auction
- Camden Council boosts mobile security